
Discrete data is usually visualized using tally charts, bar charts, and pie charts. Another example of discrete quantitative data could be the number of visits to your website you could have 150 visits in one day, but not 150.6 visits. The number of children is fixed-it’s not possible for them to have, say, 3.2 children.

For example, if a person has three children, this is an example of discrete data. When you count something, you get discrete data. These values are fixed and cannot be broken down. Discrete dataĭiscrete data is quantitative data that can only take on certain numerical values. There are two main types of quantitative data: Discrete and continuous. What are the different types of quantitative data?
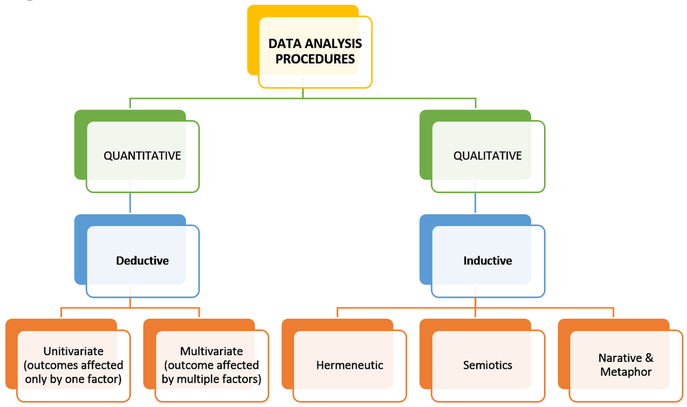
Now we know the difference between the two, let’s get back to quantitative data. Examples of quantitative data include numerical values such as measurements, cost, and weight examples of qualitative data include descriptions (or labels) of certain attributes, such as “brown eyes” or “vanilla flavored ice cream”.Quantitative data lends itself to statistical analysis qualitative data is grouped and categorized according to themes.

What are the different types of quantitative data?.What’s the difference between quantitative and qualitative data?.What is quantitative data? (With examples).We’ll also show you what methods you can use to collect and analyze quantitative data.īy the end of this post, you’ll have a clear understanding of quantitative data and how it’s used. We’ll explain exactly what quantitative data is, including plenty of useful examples. In this post, we’ll focus on quantitative data. If you plan on working as a data analyst or a data scientist (or in any field that involves conducting research, like psychology), you’ll need to get to grips with both. In simple terms, quantitative data is measurable while qualitative data is descriptive-think numbers versus words. Data professionals work with two types of data: Quantitative and qualitative.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
